
Radiology
Radiology is a medical specialty that involves the use of medical imaging to diagnose and treat illnesses in both animals and humans.
To diagnose or treat illnesses, a range of imaging techniques are utilised, including X-ray radiography, computed tomography (CT), ultrasound, nuclear medicine, including positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and fluoroscopy. Interventional radiology is the practice of performing minimally invasive medical operations under the supervision of imaging technology such as those listed above.
The current practice of radiology entails the collaboration of a number of different healthcare professionals. A radiologist is a medical practitioner who has undergone post-graduate training who evaluates medical pictures, conveys results to other physicians by report or verbally, and performs minimally invasive medical treatments using imaging. The nurse is responsible for the care of patients before and after imaging or operations, including vital sign monitoring, drug administration, and sedated patient monitoring. A radiographer, sometimes known as a “radiologic technologist,” is a specifically educated healthcare practitioner who creates medical pictures using advanced equipment and positioning procedures for interpretation by a radiologist.
Diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology are two subspecialties of radiology.
Diagnostic radiology allows doctors to view within your body’s components. Diagnostic radiologists are doctors who specialise in the interpretation of these pictures. The radiologist or other physicians can use the diagnostic pictures to determine the reason of your symptoms, evaluate how well your body is reacting to therapy for your disease or condition, and test for various illnesses including breast cancer, colon cancer, or heart disease.
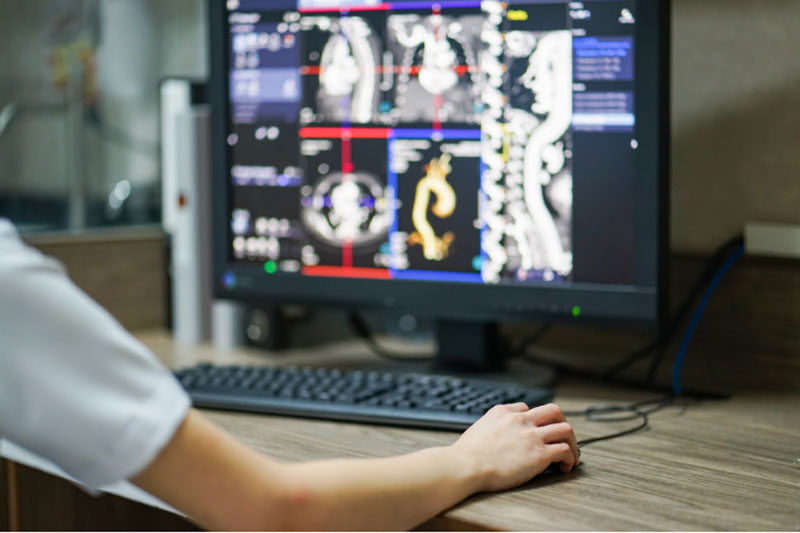
The most frequent diagnostic radiological tests are computed tomography (CT), also known as a computerised axial tomography (CAT) scan, which includes CT angiography; fluoroscopy, which includes upper GI and barium enema; and fluoroscopy, which includes upper GI and barium enema. Mammography; Nuclear medicine, which includes tests like a bone scan, thallium heart stress test and thyroid scan; Plain x-rays, which includes chest x-ray; Positron emission tomography, commonly known as PET imaging, PET scan, or PET-CT when paired with CT; and Ultrasound are also Diagnostic radiology exams.
Interventional radiologists employ imaging techniques including CT, ultrasound, MRI, and fluoroscopy to aid in the guidance of treatments. When placing catheters, cables, and other small objects and gadgets into your body, the imaging aids the clinician. This usually results in lesser incisions (cuts). Instead of peering into your body with a scope (camera) or performing open surgery, doctors may utilise this technology to identify or treat diseases in practically any region of the body. Interventional radiologists are frequently involved in the treatment of malignancies or tumors, artery and vein obstructions, uterine fibroids, back discomfort, liver disorders, and renal difficulties. It is important to consult the best radiologist near you if you are suffering from any of the above-mentioned symptoms.
Many lives can be saved by early detection. As a result, a radiologist is crucial to your health care. The radiologists at Medharbour are highly trained experts who specialise in interpreting the findings of numerous imaging procedures. Our top focus is to offer a comprehensive diagnosis so that the best therapies may be implemented. Get diagnosed and treated with the best radiology center near you.
Our Services
- Spine
- Shoulder Elbow Wrist
- Knee & Hip
- Foot & Ankle
- Sports Injuries
- Pain Management
- Neuro Rehab
- Interventional Neurology
- Residential Care
- Breast Rehab
- Gastroentrology
- Nephrology
- Radiology
- Pathology
- Cardiovascular Treatments
- Geriatric Rehab
- General Medicine
- Diabetes Care
- Gynaecology
- Pulmonary Rehab
- ENT
- Shoulder Elbow Wrist
- Ayurveda & Naturopathy
- Cancer Care
- Plastic Surgeries
- Dental Care
- Yoga
- Psychology
- Dermatology
- Hair Transplant
- Wellness Fitness
