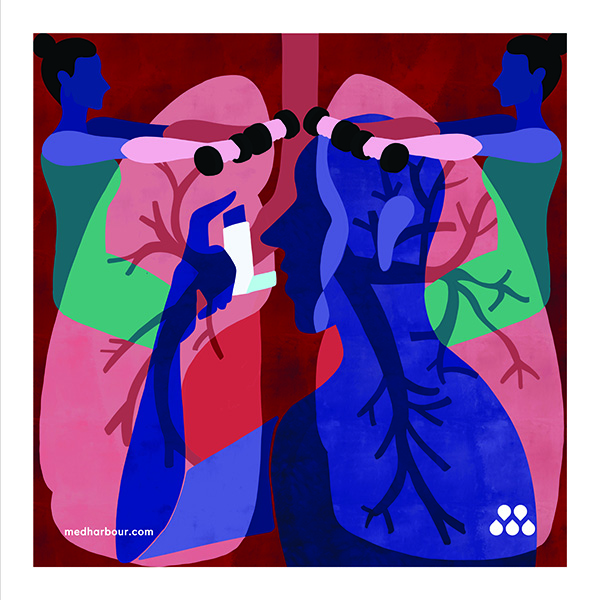
Pulmonary Rehabilitation (Lungs)
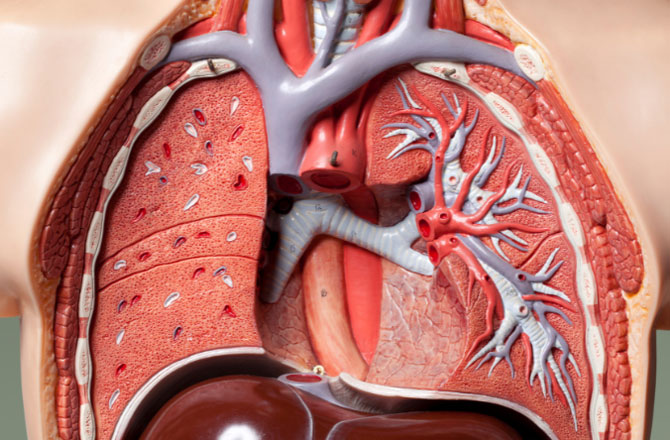
The lungs are a pair of air-filled, spongy organs on either side of the chest (thorax). Through its tubular branches, known as bronchi, the trachea (windpipe) transports breathed air into the lungs. The bronchi then branch out into smaller and smaller branches until they are tiny.
The bronchioles finally finish in alveoli, which are clusters of small air sacs. The oxygen from the air is taken into the blood in the alveoli. The waste product of metabolism, carbon dioxide, flows from the bloodstream to the alveoli, where it may be exhaled. The interstitium is a thin layer of cells that lies between the alveoli and contains blood veins and cells that support the alveoli.
The following diseases can damage the airways (bronchi):
- Asthma causes wheezing and shortness of breath because your airways are continually irritated and may spasm. Asthma symptoms can be triggered by allergies, infections, or pollutants.
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is a lung illness in which you are unable to exhale normally, causing breathing difficulties.
- Chronic bronchitis is a kind of COPD that causes a persistent wet cough.
- Emphysema: This type of COPD causes air to become trapped in your lungs due to lung deterioration. Its defining feature is the inability to blow air out.
- Acute bronchitis: A virus is typically to blame for this abrupt inflammation of your airways.
The following are examples of lung disorders that damage your alveoli:
- Pneumonia is an infection of the alveoli caused by bacteria or viruses, such as the COVID-19 coronavirus.
- Tuberculosis is a progressive pneumonia caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Lung cancer is a kind of cancer that affects the lungs. It can take many different forms and begin in any area of your lungs. It usually occurs in or around the air sacs in the major section of your lung.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung damage caused by a major disease. One example is COVID-19. Many persons with ARDS require the assistance of a ventilator to help them breathe until their lungs heal.

Pulmonary rehabilitation is an extensive intervention based on a comprehensive patient assessment accompanied by patient-tailored therapies such as exercise, education, training, and behaviour change, all of which are aimed at improving the psychological and physical condition of people with chronic respiratory disease and promoting long-term adherence to health-promoting behaviours. There are pulmonary rehabilitation centers that provides chest physiotherapy, COPD treatment and medications that are helpful to patients.
Here, At Medharbour, you’ll be guided through your experience on how to enhance your general health and well-being while lowering your risk of future pulmonary episodes. Get your disease diagnosed and treated by the pulmonary rehabilitation specialist. Breathing and relaxation techniques, increasing your energy level, changing your physical exercise habits, participating in exercise reconditioning sessions, oxygen dosage, and learning about nutrition, illness processes, respiratory drugs, energy conservation strategies, oxygen treatment, and exercise techniques will all be part of the rehab. You will get the best Pulmonary physiotherapy and rehabilitation here at our center.
Our Services
- Spine
- Shoulder Elbow Wrist
- Knee & Hip
- Foot & Ankle
- Sports Injuries
- Pain Management
- Neuro Rehab
- Interventional Neurology
- Residential Care
- Breast Rehab
- Gastroentrology
- Nephrology
- Radiology
- Pathology
- Cardiovascular Treatments
- Geriatric Rehab
- General Medicine
- Diabetes Care
- Gynaecology
- Pulmonary Rehab
- ENT
- Shoulder Elbow Wrist
- Ayurveda & Naturopathy
- Cancer Care
- Plastic Surgeries
- Dental Care
- Yoga
- Psychology
- Dermatology
- Hair Transplant
- Wellness Fitness
